We have been sampling Air Quality for about 10 years now and follow National Standards in conducting the collections of these samples. We understand the protocols written were to protect both the company that performs the remediation and the occupant of the structure being tested. We also understand the protocol.
When a structure has been treated and remediation is complete and the HVAC has been turned off, all the windows and doors have been closed and no outside air is allowed to enter the structure, we lock the door and wait.
Air sample collection is usually performed 24 to 48 hours after a remediation has been completed and the testing company should in ALL cases be the first to enter the structure after closing the remediation.
WHY is this the protocol? Very simple. We do not want any outside pollutants to contaminate our (in most cases) costly air sample testing to prove the work we have completed was correct. Remediation companies (like all companies) like to get it right the first time.
What is an outside pollutant? Any air, dust, dander, dirt that comes in from the outside.
How can the pollutants get in the structure? An open door, window, attic, crawl space, basement or HVAC system running will pull outside air into your home. Bottom of shoes, on clothes and on pets that go in and out of your home.
So why would I ever use an ERMI test to test my home that requires settled dust particles weeks or even months after a remediation has been conducted?
From EM Lab P&K website:
ERMI Testing Lab Services
What Is ERMI? The Environmental Relative Moldiness index (ERMI) was developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development (ORD) as a research tool to investigate mold contamination in homes. The methodology is based on using mold-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (MSQPCR) to quantify 36 molds and calculate an index number for comparison with a database of reference homes. EMLab P&K was one of the first collaborators to help establish the reference database and continues to offer this service to clients for the identification of mold problems in some buildings.
Disclaimer: The EPA has not endorsed or validated any tools or methods to determine mold burden in homes including MSQPCR and ERMI. The EPA licensed this test to laboratories including EMLab P&K. However, the transfer of this technology under the Federal Technology Transfer Act cannot be used to make any claims suggesting that the ERMI is an EPA-approved or validated test. (Source: EPA, Office of Inspector General: Public May Be Making Indoor Mold Cleanup Decisions Based on EPA Tool Developed Only for Research Applications).
NOTE: View the sample report for EMLab P&K’s ERMI testing service.
ANALYTICAL SERVICES
How Does ERMI Work?
The ERMI test involves the analysis of a single sample of dust from a home. The sample is analyzed using mold-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (MSQPCR), a highly specific DNA-based method for quantifying mold species. A simple algorithm is used to calculate a ratio of water damage-related species to common indoor molds and the resulting score is called the Environmental Relative Moldiness Index or ERMI. The ERMI value is typically between -10 and 20.
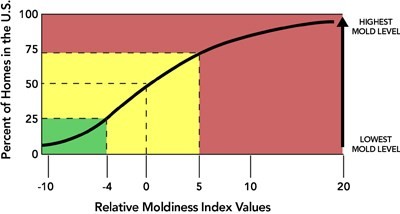
National Relative Moldiness Index Values
In order to most effectively use this new tool, the ERMI must be compared to a national database. Indices were determined using this method for 1,096 homes across the U.S. as part of the 2006 HUD American Healthy Home Survey. Individual indices, ranked from lowest to highest were used to create a national Relative Moldiness Index (RMI) Scale.
How Was ERMI Developed?
In initial studies by the EPA, the concentrations of different mold species in “moldy homes” (homes with visible mold growth or a history of water damage) and “reference homes” (homes with no visible mold) were compared. Based on those results, mold species were selected and grouped into those with higher concentrations in moldy homes (group 1) and those with lower concentrations (group 2). To calculate the ERMI, all concentrations are log-transformed and the sum of group 2 is subtracted from the sum of group 1.
What Are The Advantages of ERMI Testing?
In addition to the simplicity of taking only one sample, the ERMI offers several advantages over traditional mold screening methods. Carpet dust acts as a reservoir for mold spores and is more representative of mold levels over time versus short-term air samples. The use of MSQPCR for this test allows for increased precision as it is based on a biochemical assay using calibrated instrumentation. Further research is being conducted and published that will link the ERMI assessing health risks for susceptible individuals. This information along with the national database will be invaluable in providing an objective and standardized method for screening homes for mold.
So how should the dust sample be collected to get a proper ERMI result?
If you are using a testing company please make sure they are only collecting a SINGLE sample of dust.
The same should hold true if you are using a kit you have received in the mail and are doing the collection yourself.
Lastly please understand; the ERMI at this point is still for information purposes only and not to be used for clearance after remediation of any kind.


Recent Comments